Over the years, you have been able to solve your specific business challenges while running your EBS application that rely on Oracle databases. You have developed them in-house, you’ve invested years into your mission-critical applications. Without them, you can’t properly manage your manufacturing, supply-chain, operations, logistics, sales and marketing. In essence, you can’t run your business without them.
You can think of running Oracle E-Business Suite on Oracle Cloud for Infrastructure as running exactly the same EBS applications that you run on premises in your data center today — the same applications you may have customized — on a combination of Oracle’s Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS). Running Oracle E-Business Suite on Oracle Cloud requires, at minimum, a subscription to the Oracle Compute Cloud Service (Compute), part of Oracle’s Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), to provide the resources you need. You can then choose to run EBS on a single node or multiple nodes. In these two scenarios, your application and database tiers both run on IaaS. Read the 10 things you need to do now before you migrate your EBS to OCI.
An alternative is to run your EBS database on Oracle’s PaaS, called Database cloud services, by subscribing to whichever of these best meets your needs on:
- Oracle’s Database Cloud Service (DBCS) or
- Oracle Database Exadata Cloud Service (Exadata CS).
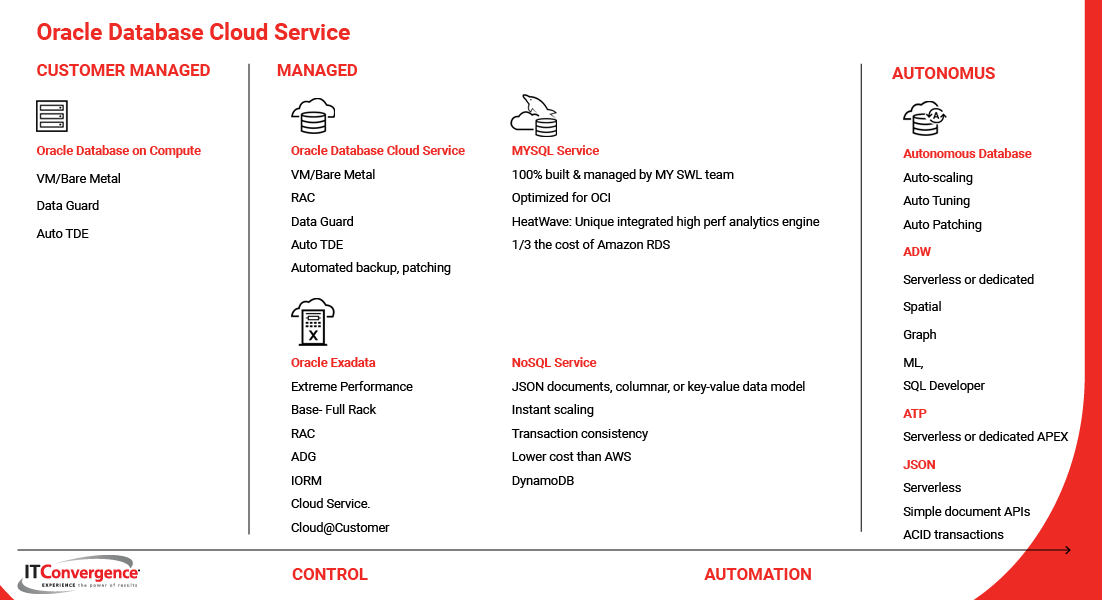
What is the Oracle Database Management Service
Oracle Cloud Database and Oracle Autonomous Database run on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, a second-generation cloud offering that runs enterprise applications and databases with exceptional performance, scalability and security. For example, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure allows customers to independently scale compute and storage resources without restarts, instantly meeting the needs of any size business
Oracle has the most complete data management portfolio for any enterprise workload. It is a high probability customers running Oracle applications will be using Oracle database services. Oracle database products offer customers cost-optimized and high-performance versions of Oracle Database, converged, multi-model database management system, as well as in-memory, NoSQL and MySQL databases. Oracle Autonomous Database, available on premises via Oracle Cloud@Customer or in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, enables customers to simplify relational database environments and reduce management workloads.
Drivers for Migrating Database from Onprem to Oracle Cloud Database Service
- Application performance problems, unable to cope with data growth
- Aging hardware, expiring support, due for renewal
- Complexity of managing security, compliance, & policies for data access onorem
- Database Administrators cannot keep up with escalating workloads
- Complex architectures to ensure High-Availability
- Disaster recovery problems, escalating costs, unacceptable RPO/RTO performance
- Costly over-provisioning of databases to prepare for peak demand
- Difficulty making databases available to all stages of Dev/Test lifecycle
- Escalating and hard-to-control cost-of-ownership problems
- Bring-Your-Own-License” (BYOL) to leverage the investment in your on-prem databases
Why Migrate the Database Along with your EBS
- Your EBS database will be on the same OCI infrastructure platform.
- Leveraging the same set of security EBS has.
- Closer to your application will mean minimum latency
Migrating EBS Data to Oracle Database Cloud Services (DBCS) will help
- Support scale-out of application and database tiers
- Leverage DBCS to improve manageability and support Oracle RAC
- Store your data in Oracle Database Cloud Service (DBCS or Exadata CS)
Secure your EBS Database on Oracle Cloud Database Management Service
- Data is encrypted by default in the cloud (in transit and at rest)
- Data is classified for risk
- Data is masked for DevTest activities
Database Use Cases for EBS
- Application development and testing – DevTest is one of the leading use cases for the public cloud. Many companies form DevOps teams in which developers collaborate with operations personnel to create, test, troubleshoot, and improve applications as part of a continuous flow.
- Sandbox environments – Some Oracle Database customers use Oracle Autonomous Database as a staging ground to practice upgrade procedures or try out new database features, such as transportable table spaces and pluggable databases. If you make a mistake, you can easily delete the database instance and start over.
- Data warehouses – Oracle Autonomous Database is ideal for data warehouse workloads, especially when a diverse or geographically dispersed workgroup needs to access analytics services. It reduces the cost and complexity of managing the infrastructure, allowing analysts to focus on extracting value from their data.
Why OCI for Your EBS database
- OCI takes advantage of high scale, high bandwidth networks that connect cloud servers to high performance local, file, block, and object storage to deliver a cloud platform that yields the highest performance for traditional and distributed applications, as well as highly available databases. In short, OCI is architected to support the applications that enterprises have been running for years, as well as those they are creating for the future. You can read all reasons to migrate your EBS to OCI
- OCI offers the ability to run everything from small VMs to large bare metal clusters and highly available databases on the same isolated networks, accessible through the same APIs and console – allowing apps to have direct, low-latency access to high-performance DBs running on physical or virtual servers in the same infrastructure.
- With OCI, businesses can run applications requiring millions of IOPs, millisecond latency, and many GB/s of guaranteed bandwidth, on a pay-per-use or monthly credit model. They can build cloud environments with equal or better performance and predictability than dedicated, on-premises environments. In fact, most customers report workloads running on OCI typically show performance results exceeding their on-premises environment.
Oracle Cloud Database Service on a Robust Platform
OCI has a number of unique features and tools that are geared to migrate and/or run Oracle’s databases and business applications portfolio with unmatched scalability and reliability. Minimal architecture changes are needed to move Oracle Applications, reducing the cost and length of migration to the cloud. Proven technologies like RAC are available, retaining best practices and confidence. And the latest hardware and technologies are available, improving database and application performance and results:
- Oracle Cloud Databases: Oracle Cloud Database scale to many times the storage capacity and performance of competitors, reaching up to 268 terabytes of capacity and millions of IOPS per instance.
- Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC): Running RAC on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure provides database High Availability (HA) with failover in seconds, performance scaling into the hundreds of thousands of IOPS, and seamless operations via rolling patches and upgrades. This offering introduces a new cloud-based standard for production database applications.
- Oracle Exadata: Run partial or full rack Exadata form factors in the same enhanced regions, and on the same virtual cloud networks as bare metal compute and other OCI services – controlled with the same set of governance tools, and accessible via the same console/APIs. Providing maximum scalability, database storage can scale to 268 terabytes and process millions of IOPS.


