Oracle continues to make progress with shifting its business model and customer base toward the cloud, albeit with variation in pace across product lines. To accelerate the movement, Oracle is has been adding more “cloud-friendly” attributes to its strategy and execution.
Understanding the Oracle Cloud Shared Responsibility Model
Cloud providers like Oracle employ best-in-class, enterprise-grade security technology and operational processes to secure the cloud services. To deploy and operate your workloads securely in Oracle Cloud, you must be aware of your security and compliance responsibilities.
You’re responsible for configuring your cloud resources securely. The following graphic illustrates the Oracle cloud shared security responsibility model:
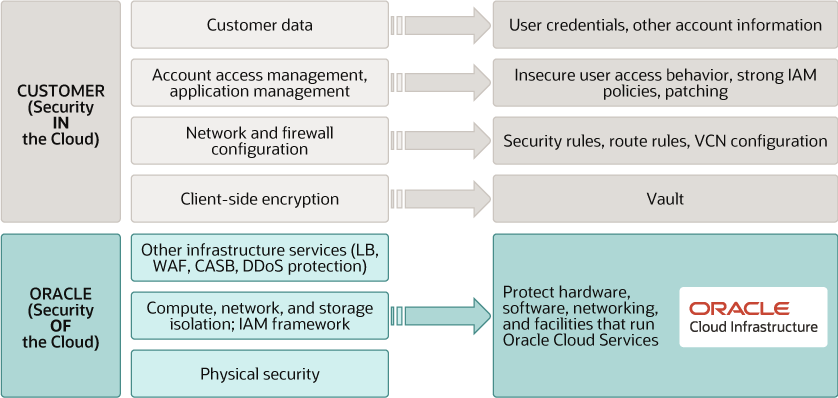
Oracle is solely responsible for all aspects of the physical security of the availability domains and fault domains in each region. Both Oracle and you are responsible for the infrastructure security of hardware, software, and the associated logical configurations and controls.
As a customer, your security responsibilities encompass the following:
- The platform you create on top of Oracle Cloud.
- The applications that you deploy.
- The data that you store and use.
- The overall governance, risk, and security of your workloads.
The shared responsibility extends across different domains:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Workload Security
- Data Classification and Compliance
- Host Infrastructure Security
- Network Security
- Client and Endpoint Protection
- Physical Security
Securing the Complete EBS Stack in Cloud
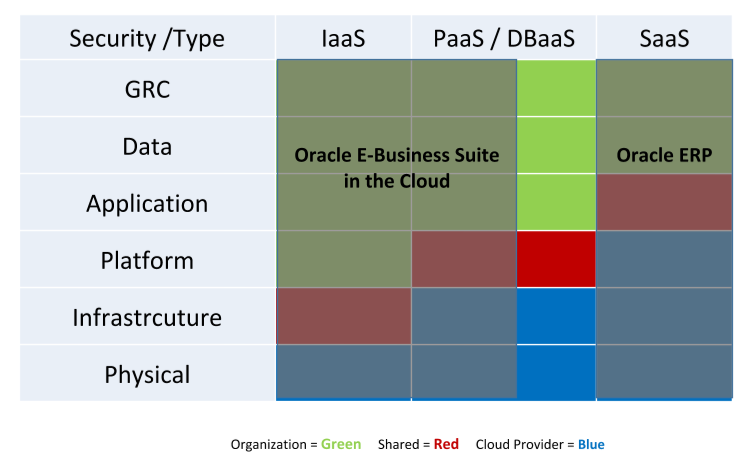
Cloud services have become an essential part of modern business, increasing both opportunities and risks. Oracle provides security features and options at every layer of the cloud.
- Technology: Robust, layered defenses span IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, extending security to the network, hardware, chip, operating system, storage, and application layers, bolstered by new security cloud services.
- Process: Security policies and controls are maintained by people and technology at physical data centers.
- People: The Oracle Cloud employs talented, industry-leading cybersecurity professionals who are trained on Oracle Software Security Assurance practices.
- Physical: Data centers are built around multi-layered physical defences designed to allow authorized people in and keep unauthorized people out.
Does EBS to OCI Change Security Responsibilities?
You are responsible regardless of where it is stored. How to ensure your security posture is intact in the cloud may differ from organization to organization and it is definitely your responsibility. The shared responsibility model is spelled out in the terms of services document of every CSP from Microsoft to Amazon or even Oracle. Even today it is arguably the least understood and most misconceived concept. Simply put, the shared responsibility model outlines the CSP’s responsibility to maintain a secure and continuously available service and enterprises’ responsibility to ensure secure use of the service.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) is designed with services and features that constitute the seven core security pillars. They are:

Design Principles for EBS Security
Apply the following design principles to deploy, operate, and use your applications securely in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure:
- Understand and implement the security services and features of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
- Understand the shared security responsibility model when assessing cloud.
- Implement the principles of least privilege and separation of duties. -Limit privileges as much as possible. Users should be given only the access that’s essential to perform their work. Review user privileges periodically to determine relevance to the current work requirements.
- Implement multilayer security mechanisms.
- Protect data at rest and in transit.
- Monitor and respond to security events. -Monitor system activity. Establish who should access which system components, and how often; and monitor those components.
- Stay up to date on security alerts, patches, and software updates.
- Implement security-related best practices.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Security
4 Pillars of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- Outstanding Price Performance
- Secure By Design – Security First OCI starts with a zero-trust architecture
- The Open Cloud for Enterprise Interoperability Deep Enterprise
- Deep Technology Experience
Oracle Cloud Security Components
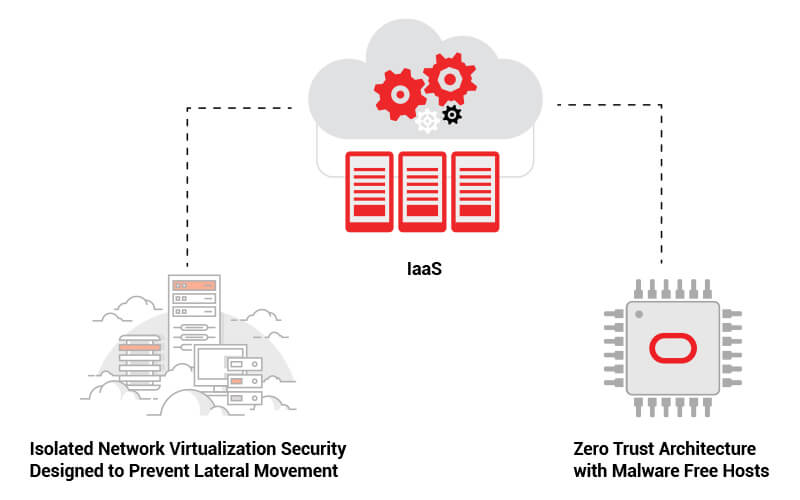
Second-generation Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) offering which was conceived and architected with security as a primary design principle has two major components
- Isolated Network Virtualization Security
- Zero Trust Architecture with Malware Free Hosts
Isolated Network Virtualization Security
Prevent attacks on customer tenancies with isolated network virtualization. A foundational element of Oracle Cloud infrastructure’s security-first architecture, Isolated network virtualization stops malware in its tracks with a custom-designed SmartNIC to isolate and virtualize the network.
-
Prevent attacks from compromising the network – This was one of the shortcomings of first-generation clouds. In first-generation cloud offerings, if a successful attack compromises a virtual machine instance and subsequently a hypervisor, there are no barriers to prevent an attacker’s attempts to modify the network. The networking function is managed by the same hypervisor that has been compromised: a virtual machine escape that gains access to the hypervisor also has access to the network. This can lead to several threats to hosts on the network and could expose private tenant data.
- Isolate and virtualize the network to prevent attacks – Here the second-generation cloud has an advantage with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, different from first-generation clouds because of its use of a custom-designed SmartNIC that isolates and virtualizes the network.
The SmartNIC is isolated by hardware and software from the host, preventing a compromised instance from compromising the network. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure maintains greater external control of host network functionality and can prevent network traversal attacks.
Zero Trust Architecture with Malware Free Hosts
As the use of cloud services rapidly expands, it also creates new potential for compromised or stolen credentials of a privileged administrator or application. Additionally, it can open the potential for data theft, and cyber criminals to conduct cyber fraud, as effective security controls are often an afterthought. Zero trust makes it possible for organizations to regulate access to systems, networks, and data without giving up control.
Work From Anywhere Productivity: Empower your users to work more securely anywhere and anytime, on any device.
Cloud Migration: Enable digital transformation with intelligent security for today’s complex environment.
Risk Mitigation: Close security gaps and minimize risk of lateral movement.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Data Protection
 Cloud Infrastructure Security with a focus on data protection and securing the paths to access sensitive data. Reduce the risk of firmware-based attacks against Oracle Cloud Infrastructure customer tenants with custom-built, hardware-based root of trust technology.
Cloud Infrastructure Security with a focus on data protection and securing the paths to access sensitive data. Reduce the risk of firmware-based attacks against Oracle Cloud Infrastructure customer tenants with custom-built, hardware-based root of trust technology.
Protect customer tenants from firmware-based attacks – Hardware technology customized to deploy clean firmware for every new tenancy. Reduce the risk of firmware-level attacks against cloud tenants with root of trust technology designed to wipe and reinstall the firmware every time a new server is provisioned or a new customer tenancy is established.
Reduce risk from attacks or backdoors in firmware – Cleans and power cycles each new server. Reduces the risk from a permanent denial of service (PDoS) attack or attempts to embed backdoors in the firmware by power cycling the hardware host, installing the firmware, and confirming the process has been performed as expected for every new server.
Oracle has put the security of critical workloads at the forefront of its cloud design. For customers running security-sensitive workloads, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure is a security-first public cloud with robust security architecture and a deep set of rich defense-in-depth capabilities to reduce risk and attack surfaces.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure has built security in the architecture, data center design, personnel selection, and in the processes for provisioning, using, certifying, and maintaining OCI infrastructure. Security First OCI starts with a zero-trust architecture.
Conclusion
The shared security model over the Cloud IaaS brings substantial responsibility on the shoulders of the customer. This can be reasonably addressed with careful planning, implementation and monitoring.
Gartner recommends to rely on the expertise of a third-party Oracle managed service provider (MSP/MSE) to fully understand all of the addressable responsibilities and capabilities of both the client organization and Oracle, guaranteeing continuity and security of their environments running on OCI.

