Key considerations
- Provide secure, high-speed connectivity between cloud resources and users and/or systems that require access
- Maintain your security posture when running your business-critical EBS and adjacent apps in Oracle Cloud utilizing:
- Cloud-native security
- 3rd party security vendors such as Fortinet and Check Point Software Technologies
With the networking and connectivity architecture achieve secure and high-speed connectivity between cloud resources and users/systems accessing them. It enables you to design a network topology that suits your requirements, with resource isolation for enhanced security and management.
For migrating EBS and database to OCI there are various networking options to choose, which you can read in this blog.
The below blog highlights design architecture for EBS running on OCI between the servers.
Cloud Network Design Models
When designing and implementing your network, the connectivity architecture is based on your requirements, and will typically fall into one of two general topologies:
- Distributed, which we’ll explore below under the context of a single availability domain. This architecture consists of a virtual cloud network (VCN) with the bastion, load balancer, application, and database hosts placed in separate subnets of VCN in a single AD
- Hub-and-spoke, which incorporates virtual security appliances. A hub-and-spoke network, often called star network, has a central component that’s connected to multiple networks around it.
Benefits this architecture can provide:
- Ensure isolation from other customers and cloud workloads
- Implement network-level isolation between web/application and database tiers
- Provide monitoring and management access to all application and database tiers
- Enable private/dedicated access from corporate campus(es) via private network links
- Guarantee low latency between the cloud environment and your data center
- Establish secure network access to the application through encrypted links over the public internet
- Facilitate private network connectivity to other systems or services hosted on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- Implement load-balancing across multiple application nodes for improved performance and availability
Networking & Connectivity Reference Architecture (General)
Note: Reach out to our experts for guidance on the below architectures customized to your organization:
| Distributed: Network connectivity reference architecture
Distributed: Network security reference architecture |
Hub-and-spoke: Fortinet Security Fabric network topology
Hub-and-spoke: Check Point CloudGuard network |
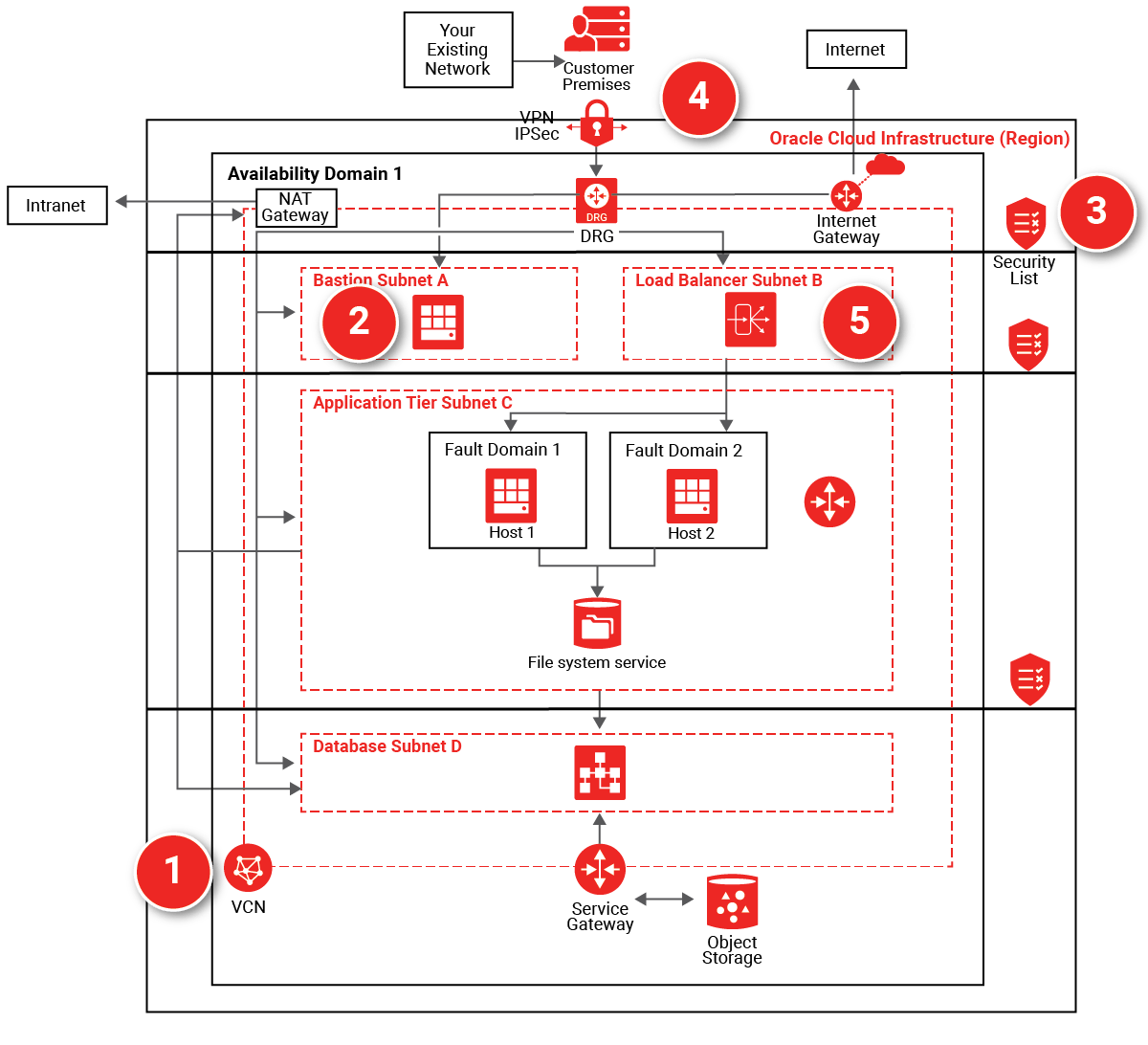
Virtual Cloud Network (1): Provides isolation for EBS from any other workload on Oracle Cloud. Subdivide using subnets and apply security rules to isolate and control access to resources.
Bastion host (2): The bastion host is an optional component that can be used as a jump server to access instances in a private subnet. You can also access the instances in a private subnet by using dynamic SSH tunneling.
Internal firewalls (3): A security list provides a virtual firewall for each tier, with ingress and egress rules that specify the types of traffic allowed in and out.
FastConnect: Multiple partners across the world offer dedicated network connections between customer premises and Oracle datacenters. This allows customers to access their EBS implementation as if it was running in their own datacenter.
IPSec VPN (4): For lower cost, but still secure access over existing Public Internet connections, customers may connect through the Dynamic Routing Gateway (DRG).
Load balancing (5): Pre-configured, redundant load-balancers are available on private and public subnets to balance traffic within the implementation and from external connections, respectively.
Other Key considerations for Designing an Oracle Cloud Architecture
Ensuring a successful EBS migration requires careful planning for designing the most appropriate design architecture. Below are the other considerations to learn before proceeding with your EBS to OCI Migration.