Application & Infrastructure leaders, planning to migrate Oracle applications to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure face substantial challenges when embarking on a full or partial migration from Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS). They must create and execute a detailed cloud architecture to successfully deploy EBS in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
- They have to prioritize conducting an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure readiness assessment in order to avoid delays and escalating costs.
- Collaboration between application, infrastructure and other functions such as business & finance is required to cement support for the desired migration path for the organization to cloud.
Questions While Designing an Oracle Cloud Architecture
- Will cloud-based solutions for EBS meet all our current requirements?
- Will the project be slow, difficult, painful, risky?
- Will cloud-based solutions address our pain-points, e.g. capacity planning, seasonal scaling, etc.?
- How does Oracle Cloud address certain specific challenges (like security)?
- Can a well designed Oracle cloud architecture help in accelerating the migration?
You should able to find answers to all the above questions as we discuss the components of the cloud architecture design and how each component can help you create a robust cloud environment.
Components of Oracle Cloud Architecture Design
1. Networking & Connectivity
Key Considerations
- Isolation from other customers
- Access from your HQ to E-Business Suite
- Private network links
- Encrypted links over public internet
- Public internet endpoints
- Private network connectivity
- Isolation between application tiers
- Monitoring, management access
- Load balancing
- Low network latency
Oracle cloud architecture prioritizes secure, high-speed connectivity between your cloud resources and users/systems that require access to those resources. It offers tools to help you design a network topology that fits your needs, allowing you to isolate resources for security and management purposes between database tiers, load balancing, bastion hosts, application tiers.
2. Resiliency & High Availability
Key Considerations
- Multiple active-active nodes at each application tier
- System resilience
- Backup strategy for non-database tiers
- Redundancy strategy for database tier
- Backup requirements for database tier
The primary objective for this component in the Oracle cloud architecture is to build resiliency, redundancy and high availability (HA) into the cloud infrastructure that is supporting E-Business Suite and its backend datasets.
3. Disaster Recovery
Key Considerations
Single region DR
- Active-active components across ADs
- Active-passive components across ADs
- Regional subnets across ADs
- Load-balancing
- Storage synchronization
- Database DR
Multi region DR
- Application replication between regions
- Storage replication between regions
- Database protection between regions
The primary objective of disaster recovery component in the cloud architecture is to ensure that you are ready for any kind of unforeseen events which would require you to failover and still keep E-Business Suite up and running.
Designing the Disaster Recovery Component of Oracle Cloud Architecture (with sample design)
4. Security and Identity
Key Considerations
- Ensure EBS and associated data assets are isolated
- Protect internet-facing applications
- Data encryption
- Segregate operational responsibilities and restrict access to cloud services
- Use existing and 3rd party security assets
- Audit and monitor actions
- Demonstrate compliance readiness
The security component in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure architecture aims to provide you with the means to preserve your security posture while operating your EBS and other integrated applications in the Oracle Cloud. Despite the reduced burden of constructing and maintaining data center infrastructure, it is still necessary to have unparalleled control and visibility over what is being run in the cloud.
5. Cost Management & Governance
Key Considerations
- Set and manage cloud budgets
- Prevent overspending
- Ensure accurate cost tracking across departments and projects
- Analyze which departments, services and projects are contributing to cloud usage over time
- Get granular usage details for invoice reconciliation
- Identify areas to optimize costs
Oracle offers cost management tools that are essential for customers transitioning from a CapEx model to an OpEx model. In the OpEx model the costs fluctuates with system usage, and customers require tools to understand, control, and communicate these cloud costs within their organization. Oracle tools meet the needs of its customers and help them effectively manage such costs.
6. Monitoring
Key Considerations
- Monitor health and capacity of cloud resources
- Optimize E-Business Suite performance in real time
- Detect and fix anomalies before they can impact your business
- Identify bottlenecks and underutilized resources
You need to be able to monitor the health and capacity of cloud infrastructure resources in order to optimize performance at all times and in real time. Objectives include ensuring availability and performance in the cloud, including the ability to detect and fix anomalies before they can impact your business. Additionally, you may require the visibility to identify bottlenecks and under-utilized resources for optimize accordingly.
Chances are, you are already leveraging monitoring tools like Oracle Enterprise Manager and Oracle Management Cloud for your existing EBS deployment. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers infrastructure monitoring natively within the console, but it can support your existing monitoring tools.
Designing the Monitoring Component of Oracle Cloud Architecture (with sample design)
7. Migration and Deployment
Key Considerations
- Application-aware tooling so you can keep existing customizations and integrations
- Post-migration application configuration
- Data migration
We understand that when it comes to migrating a complex, highly customized and deeply integrated application like EBS, it’s important to do it with as little re-architecture as possible so that there’s limited downtime and the transition is completely seamless for end-users.
Designing the Migration and Deployment Component of Oracle Cloud Architecture (with sample design)
Significant Benefits of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
Most on-premises deployments can be migrated to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure without requiring significant re-architecture, re-integration nor business process changes, and will result in a solution that is more flexible, more reliable, and delivers higher performance at a lower cost than deployments running on-premises or with other cloud providers.
Operating EBS in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure can be up to 38% less than running it on-premises. Significant savings come from eliminating upfront hardware, ongoing facilities, IT administration and support costs. Oracle also estimates that EBS costs upto 44% less on Oracle than on Amazon Web Services (AWS).
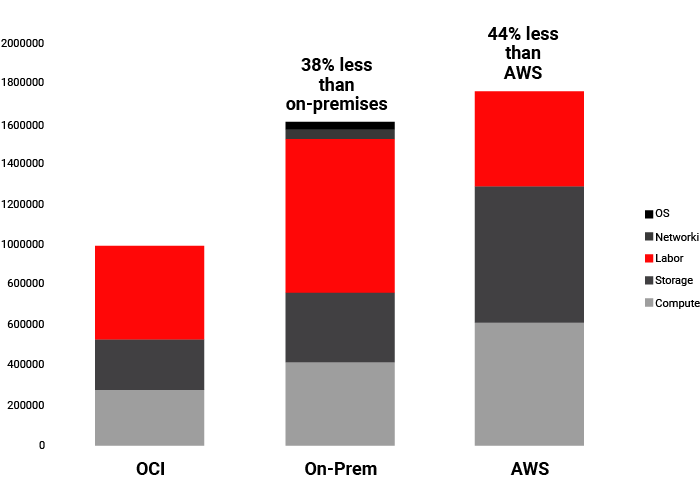
There are also significant performance benefits when you run on Oracle’s cloud.
- OCI’s unique non-oversubscribed networks and single-tenant offerings like bare metal compute and Exadata ensure consistent performance.
- Customers have experienced upto 30-50% performance improvements.
- Unlike other clouds, OCI also offer service level agreements to back up performance guarantees.
Additionally, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers unique infrastructure capabilities, tools and support that are optimized for Oracle applications.
- At the highest level, Oracle tests on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and not on any other cloud.
- EBS Cloud Manager is available only for workloads running in the Oracle Cloud to help streamline migration and ongoing lifecycle management.
- And then there are single vendor support advantages to running your Oracle application and database on Oracle’s cloud infrastructure.
Oracle professional services and ecosystem certified cloud MSE/MSP partners can assist to make your move as seamless as possible. IT Convergence is one of the select few Oracle cloud certified partners in North America which can accelerate a successful migration journey for you. Check out the key considerations in choosing a migration partner here.
Finally, Oracle has designed the core cloud services with enterprise applications in mind, to deliver the same level of control you are accustomed to having with your on-premises environment. Customers can leverage Oracle’s flexible compartment structure, Virtual Cloud Networks (VCNs) and bare metal compute so you don’t have to sacrifice control nor change your business processes.
Lower TCO than running on-premises or other clouds
- Save 38% versus on-premises and 44% versus AWS
- Superior Performance backed by SLAs
- 30% improved performance
- 2-10x faster reporting
Automate Migration & Lifecycle Management
- EBS Cloud Manager only available on Oracle Cloud
Unique Capabilities for availability, security, control
- Reference Oracle Cloud architecture
- Leverage familiar tools for governance and control
- End-to-end testing and single vendor support
Learn more
Blueprint: Oracle E-Business Suite on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure for up to 5,000 users

